Volatility Ahead?
Hedge Smart with Options
Hedge Like a Pro:
— 3 Option Strategies for Market Uncertainty
*Not financial advice. Investment carries risk.
This advertisement has not been reviewed by the Monetary Authority of Singapore.
U.S. equities extended their rally in July, rebounding over 30% and 40% from April lows. The rally was fueled by AI optimism, paused tariffs, and strong earnings.
However, August may bring heightened volatility. Historically, returns are mixed in August and weak in September. Although the medium- to long-term outlook remains broadly positive, a number of Wall Street strategists are warning of a potential near-term pullback.
Goldman Sachs warns of a near-term pullback, citing overly bullish sentiment and rising retail activity. Morgan Stanley sees a 5–7% correction but views it as a tactical buying opportunity. Former Goldman strategist, Scott Rubner remains optimistic for August due to buybacks but advises hedging for September. JPMorgan expects momentum through Nvidia’s August 28 earnings but flags it as a possible turning point.
For investors with gains, options strategies may help hedge risks and protect profits as market uncertainty rises. Let's review some option strategies that may be useful during a correction or volatile market.
1 voucher
Source: Option Alpha
✅ Pros:
Generates additional income (option premium)
Partially reduces the effective cost basis of the stock
No additional margin required
Performs well in range-bound or moderately bullish markets
❌ Cons:
Caps upside gains at the strike price
Limited downside protection (equal to the premium received)
Risk of early assignment if the option becomes deep in the money
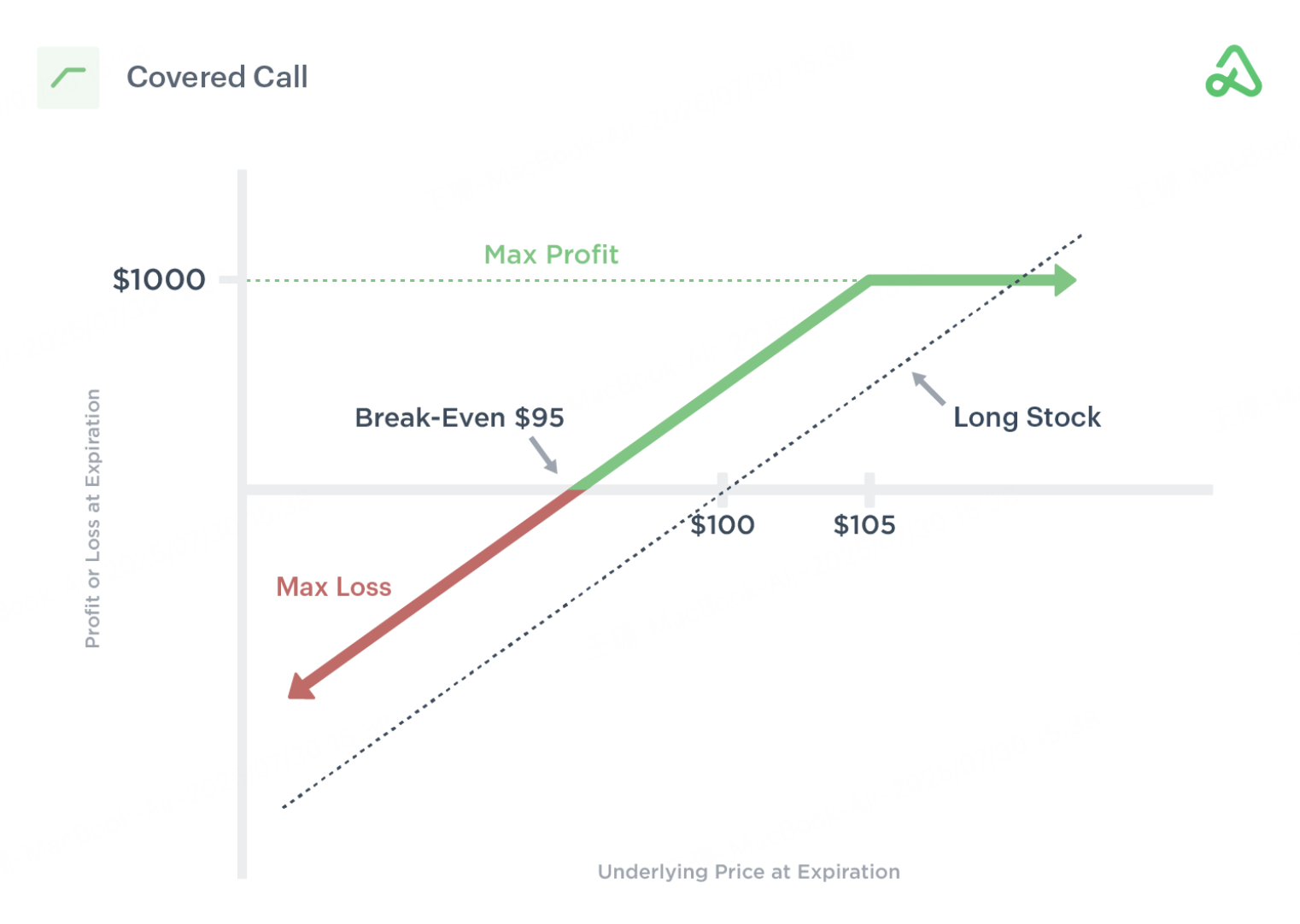
A Covered Call involves holding a stock position and simultaneously selling a call option on the same stock. This strategy is designed to generate additional income through option premiums while setting a predetermined exit level for profit-taking.
Why Use It: Earn extra income while holding your stock. But, your profit is capped if the stock price rises too much.
How To Do It:
Hold 100 shares of the underlying stock
Sell 1 out-of-the-money (OTM) call option (strike price typically 5–10% above the current market price)
Example:
Hold 100 shares of Stock A, Current Price: $200
Action: Sell 1 August expiry call option with a $220 strike price for a $5 premium per share
→ Premium received: $500
At Expiry:
If price ≥ $220: Stock is called away at $220. Profit = stock gain + $500 premium
If price < $220: Option expires worthless; investor retains shares and the $500 premium
Tips:
Select a strike price aligned with your target exit level
This strategy does not provide full downside protection if the stock declines sharply
Source: Option Alpha
✅ Pros:
Strong downside protection
Unlimited upside remains intact
Helps guard against sudden crashes or gap-down risks
Provides a predefined exit point
❌ Cons:
Premium cost reduces net profit
Time-limited: the option will eventually expire
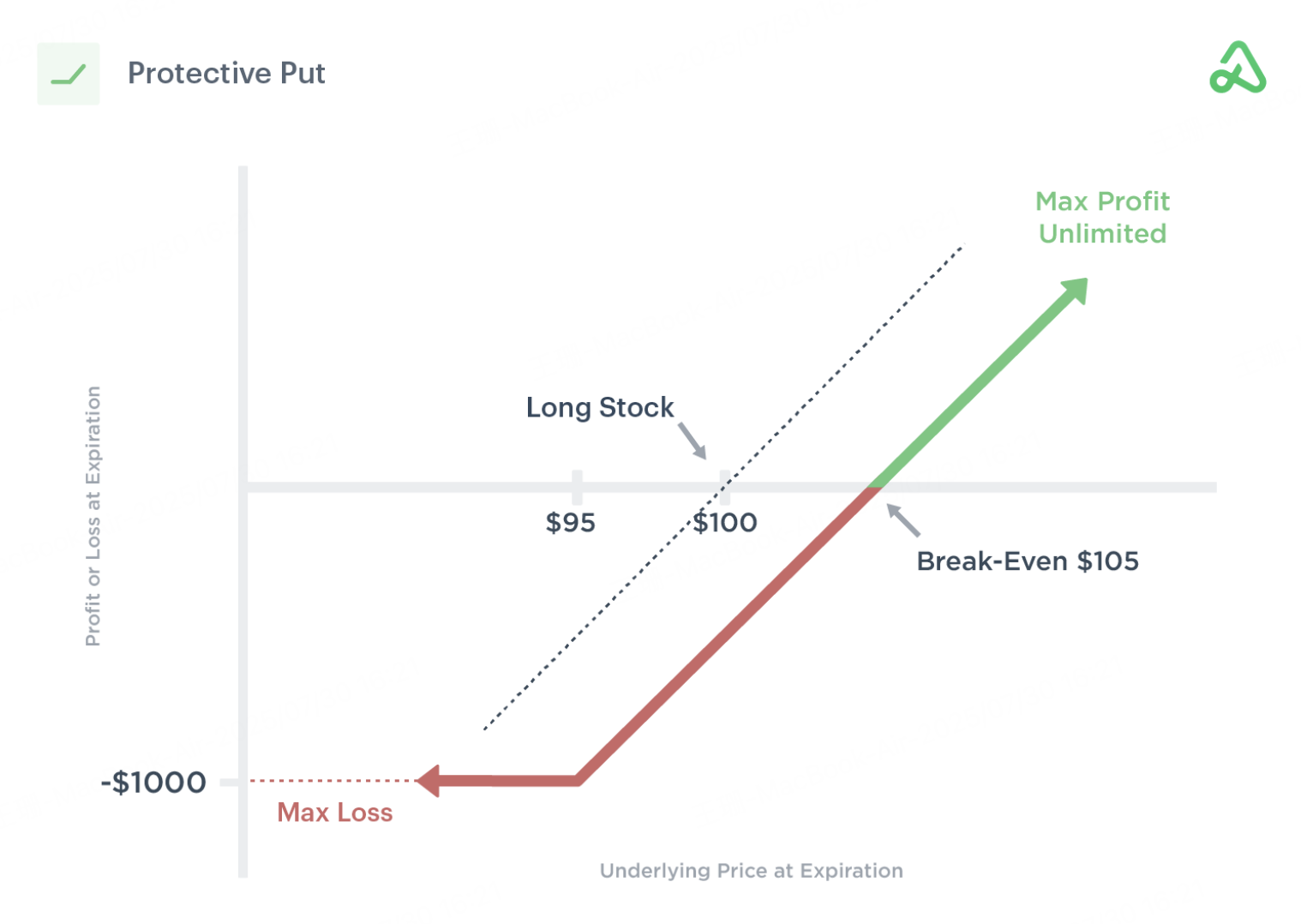
When investors hold stocks with unrealized gains but worry about near-term downside risk, they can buy Protective Put options. This strategy acts like insurance—if the stock drops below the strike price, the investor can sell the stock at the predetermined level to protect gains or limit losses.
Why Use It: Locks in a minimum exit price if the market turns, while keeping upside open for paying a premium.
How To Do It:
Hold 100 shares of the underlying stock
Buy 1 out-of-the-money (OTM) put option (strike price typically 5–10% below the current price, but above cost basis)
Example:
Hold 100 shares of Stock A, with a cost basis of $160.
Action: Buy 1 put option with a $185 strike price, expiring end of August, paying $4 per share in premium.
→ Pay total $400 as “insurance”
At Expiry:
If stock > $185: The option expires worthless, and investor continue holding the stock.
If stock ≤ $185: The option is exercised, and investor sell the shares at $185, locking in gains.
Tips:
Protective puts cost money (the premium), which increases total holding cost.
Source: Option Alpha
✅ Pros:
Defined downside protection
Clear exit levels on both upside and downside
May offer protection even during market gaps or flash crashes
Low- or zero-cost hedge depending on option pricing
❌ Cons:
Caps potential upside gains (both directions are limited)
May face early assignment on in-the-money call options
Time-limited protection due to option expiry
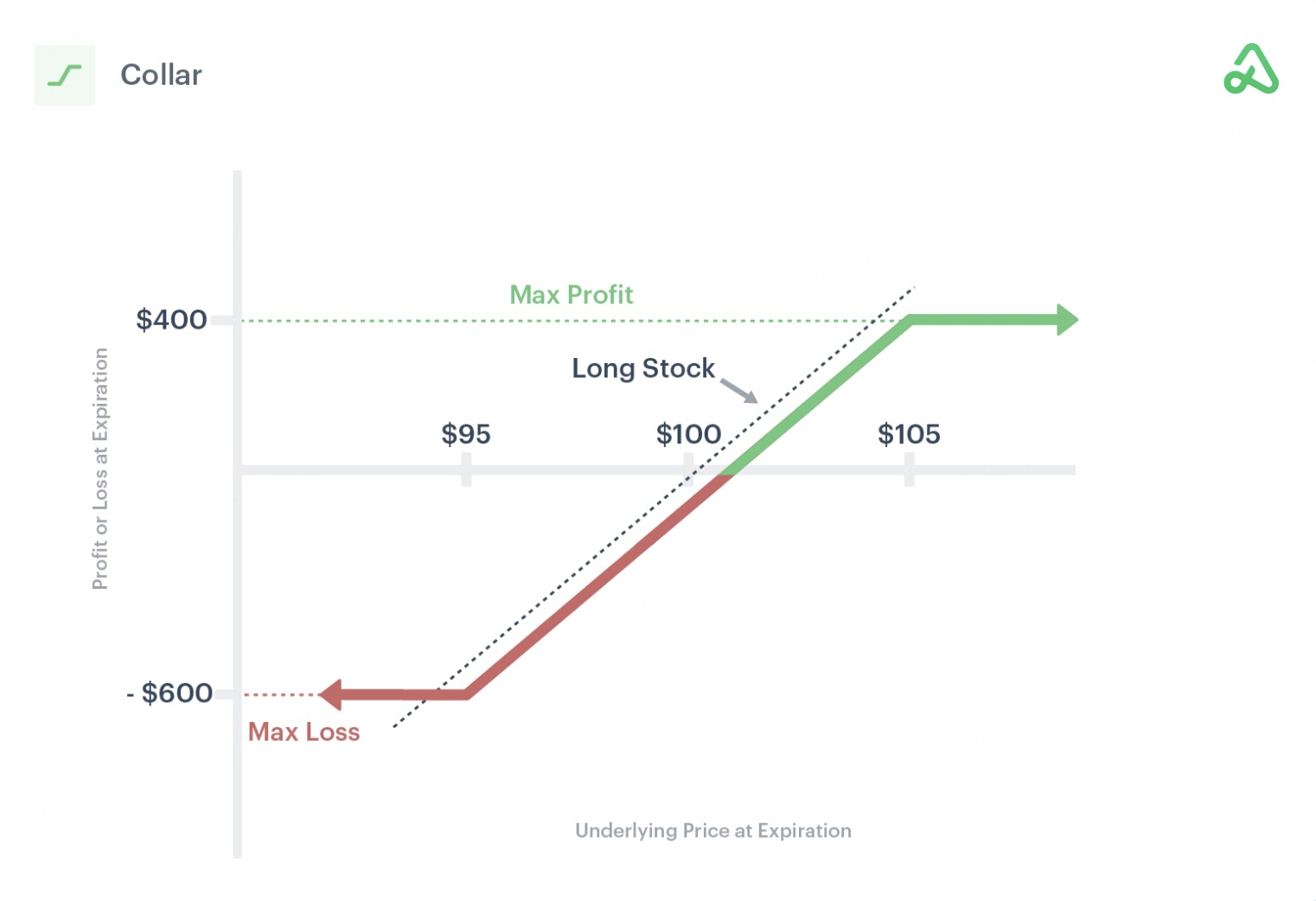
A Collar combines the benefits of a Covered Call and a Protective Put. You sell a covered call to collect premium, and use that income to pay for a protective put, creating a low-cost or zero-cost hedge. All contracts must share the same expiration and underlying quantity.
Why Use It: Sell a call and buy a put simultaneously while holding the stock. Balance downside protection with reduced or zero cost.
How To Do It:
Hold 100 shares of the underlying stock
Sell 1 OTM call and buy 1 OTM put (same expiry, same quantity)
Strike relationship: Call strike > current price > Put strike
Example:
Hold 100 shares of Stock A, Current Price: $200
Action: Sell 1 call with a $220 strike for $5/share → collect $500
Buy 1 put with a $185 strike for $4/share → pay $400
→ Net credit: $100
At Expiry:
If $185 ≤ stock ≤ $220: Both options expire worthless, you continue holding the stock.
If stock ≥ $220: The call is exercised, and shares are sold at $220.
If stock ≤ $185: The put is exercised, and shares are sold at $185.
Tips:
While this strategy provides downside protection, it caps upside gains at the call’s strike price.